Profile Video









Meet Sanders Anderson, the mastermind behind BeTrue Design. This a short video we shot to tell the story and philosophy of BeTrue Design. Be True is a highly creative branding and design consultancy in Portland, Oregon. Be True Design creates meaningful touch points for our clients that sharpen focus, add value, and leave lasting impressions.
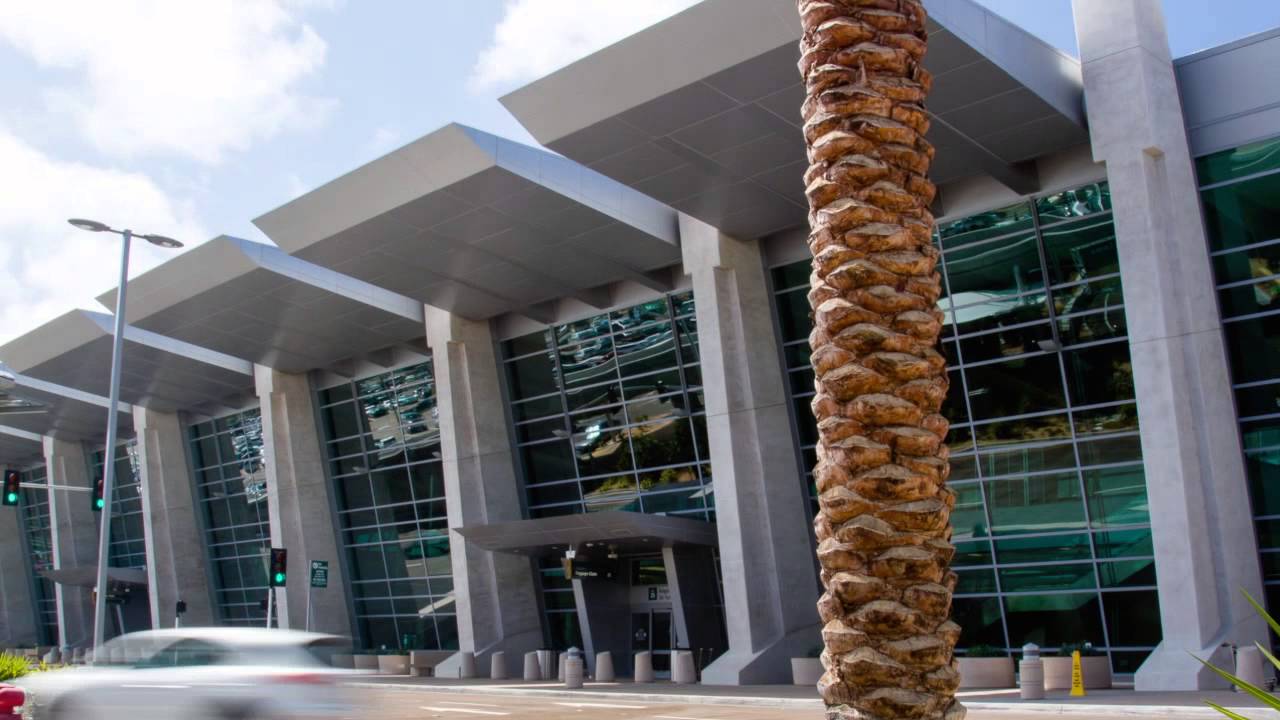
San Diego International Airport’s expansion of Terminal 2, known as The Green Build opened in August 2013. The project adds 10 new gates, a dual-level roadway and additional aircraft parking. These improvements will meet the airport’s needs until we reach about 20 – 21 million passengers annually. (In 2014, the airport accommodated nearly 19 million passengers.)
Everyday Energy is a solar energy company that specializes in development, design and installation of solar energy systems on multifamily affordable housing properties. We are a full service solar provider.
J Craig Venter Institute - Net-Zero Energy Labratory
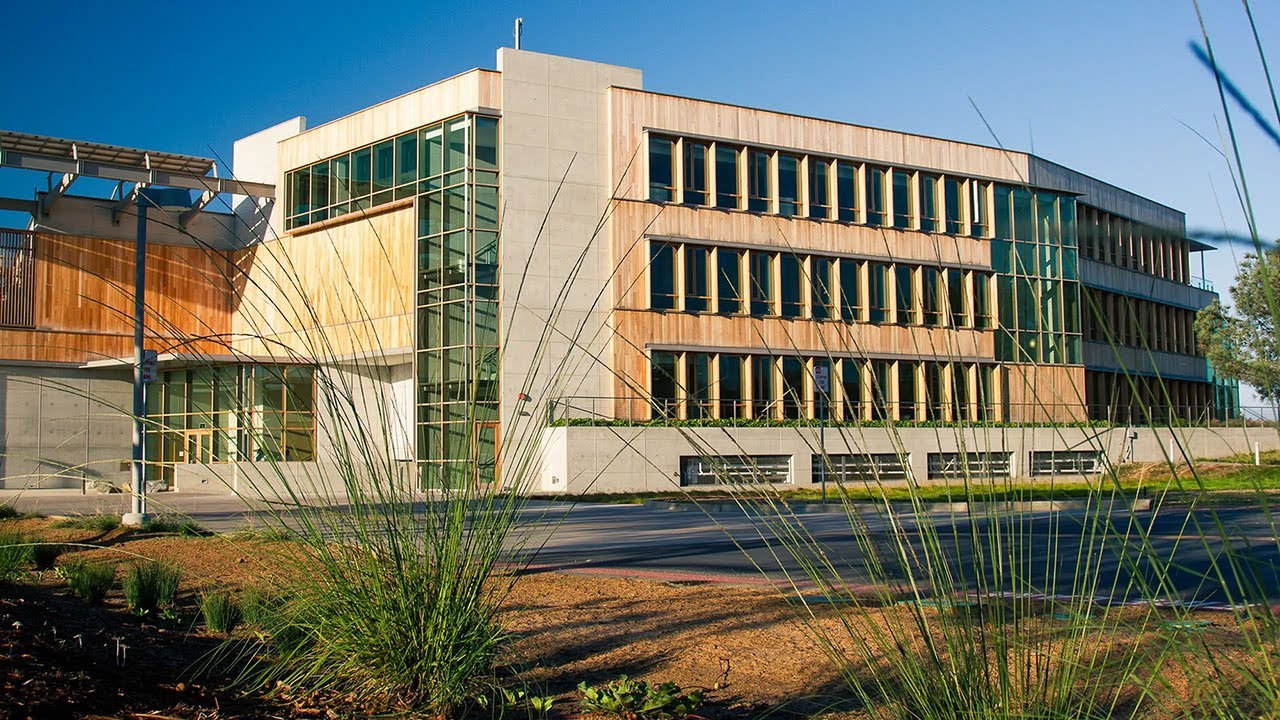
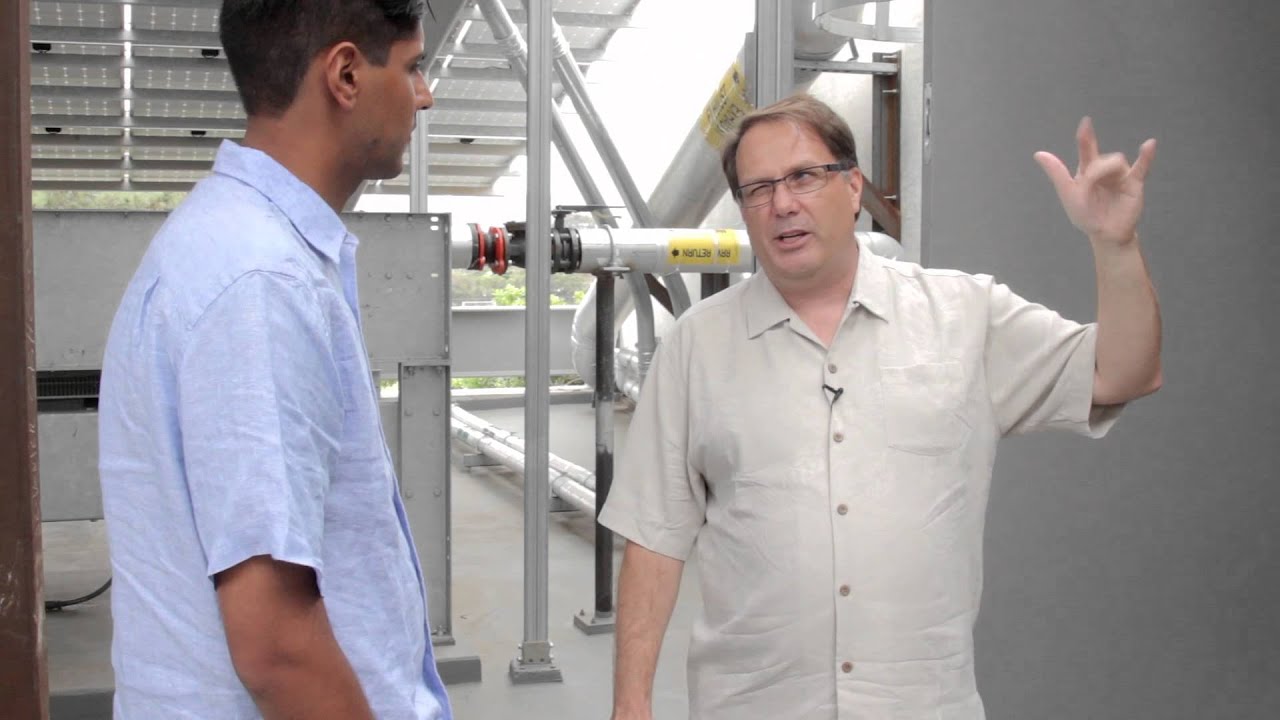
















One of the goals for building the J. Craig Venter Institute as a net zero energy laboratory was to set an example and inspire others to adopt similar practices in their facilities. This module emphasizes the project’s intent and how this intent shaped the overall design and functionality of the space.
One of the goals for building the J. Craig Venter Institute as a net zero energy laboratory was to set an example and inspire others to adopt similar practices in their facilities. This module emphasizes the project’s intent and how this intent shaped the overall design and functionality of the space.
One of the goals for building the J. Craig Venter Institute as a net zero energy laboratory was to set an example and inspire others to adopt similar practices in their facilities. This module emphasizes the project’s intent and how this intent shaped the overall design and functionality of the space.
The Location & Transportation category rewards projects that locate buildings in areas that take the community and people into account. These locations include connections and linkages to local amenities and services, provide opportunities for alternative transit, and encourage compact development. Sustainable sites focuses on a site’s relationship to the environment surrounding the building and awards credits that emphasize the buildings relationship to the ecosystems.
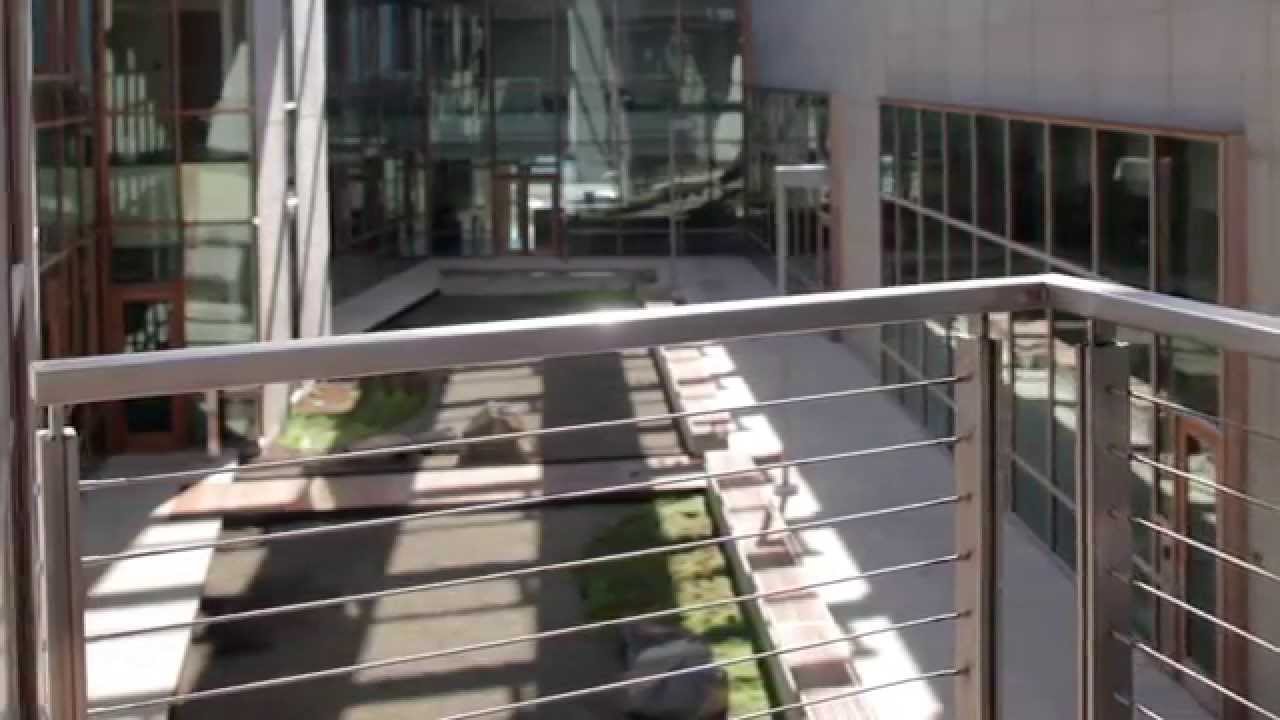
This module looks at both credit categories and discusses the location of Institute in close proximity to University of California San Diego, Scripps Research Institute, Salk Institute, and La Jolla’s vibrant biotech and research community. We also look at the building’s inclusion of a naturally ventilated underground parking garage reducing building footprint and heat island effect, and providing facilities to promote alternative transportation with showers, bike racks, and even surf racks to promote fitness. This module also discusses how the architectural design maximizes a small site footprint, the rainwater collection and storage system, and strategies taken to protect the ecological preserve and nearby ocean adjacent to site.
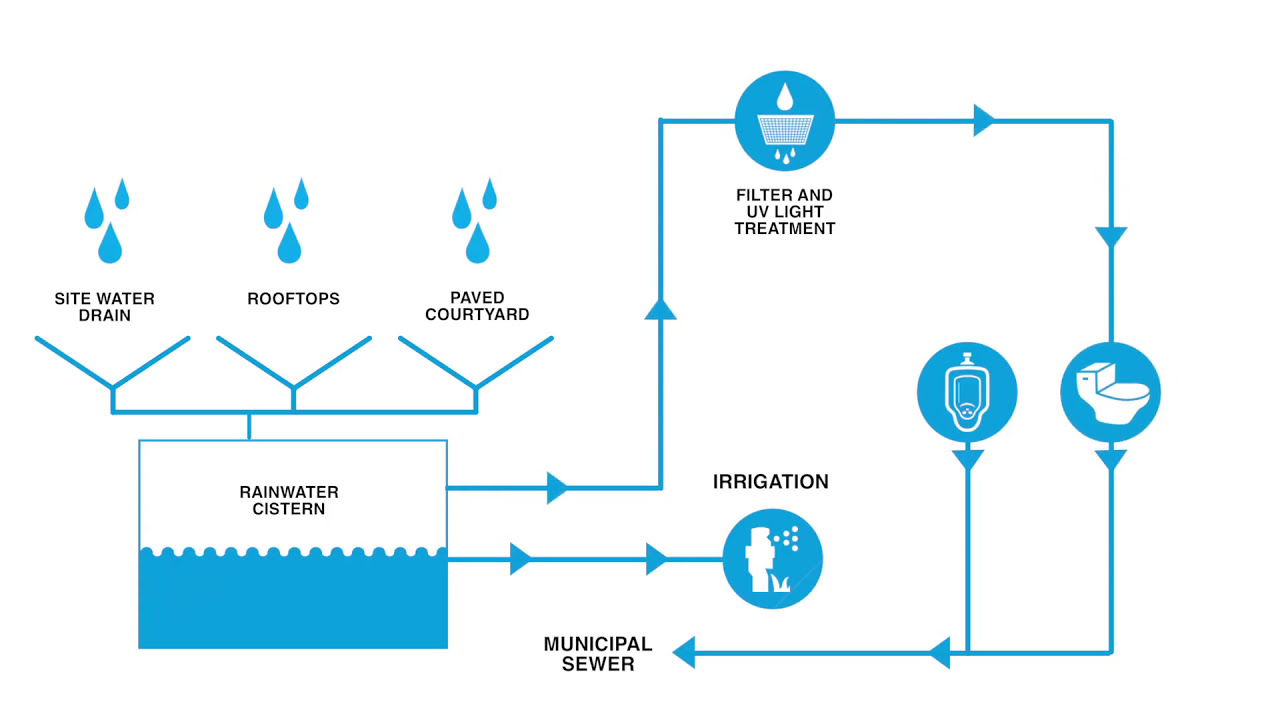
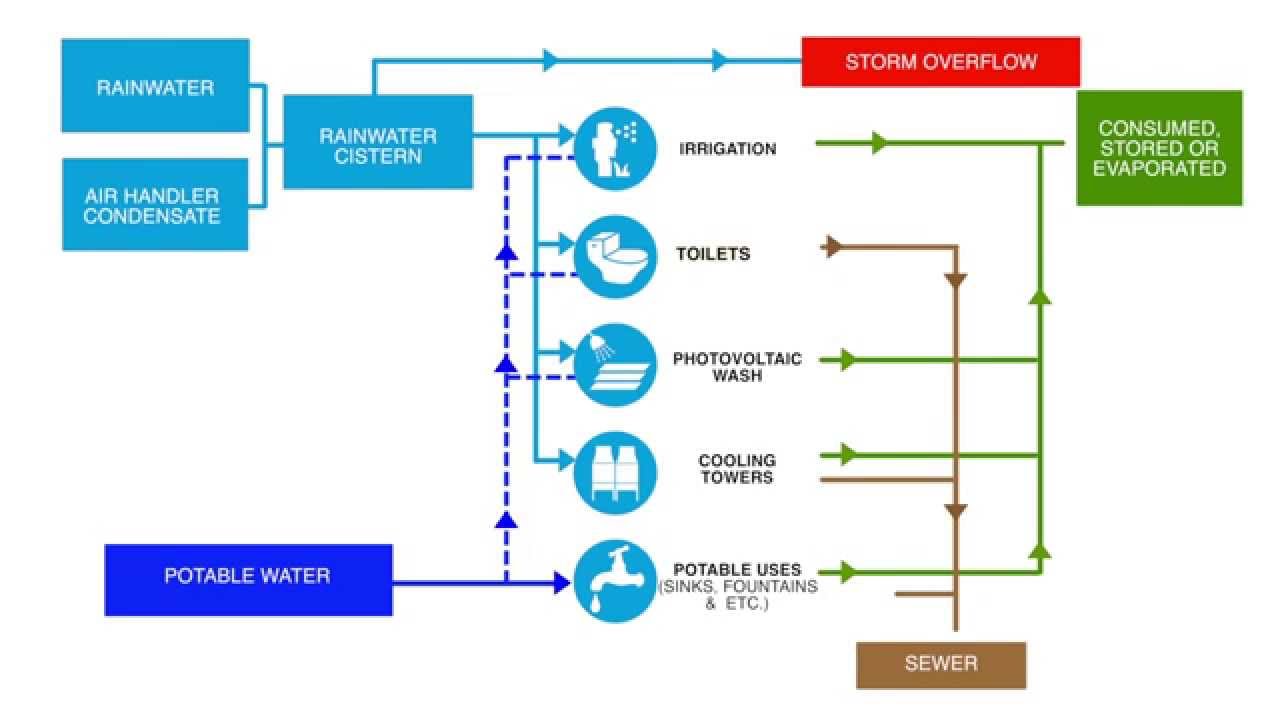
As a highly populated coastal community with an arid climate receiving, on average, only 10 inches of rain each year, the ability to increase water efficiency and leverage technologies to create alternative water solutions is vital. This is especially true in facilities, such as laboratories, which use a significant amount of water. This module highlights the various solutions used in this facility to ensure water efficiency prerequisites were met while focusing on achieving a 2/3 water reduction over a typical laboratory. Solutions discussed include low water landscaping, low flow fixtures, grey water toilet systems, waterless urinals, cooling towers operating at night, condensate collection from cooling towers and solar array, and rainwater collection. This module also discusses how the Venter Institute has prepared itself to incorporate purple pipe, grey water, and blackwater systems when implementing municipality and regulatory changes.
As a highly populated, coastal community with an arid climate receiving on average only 10 inches of rain each year the ability to increase water efficiency and leverage technologies to create alternative water solutions is vital. This is especially true in facilities, such as laboratories, which use a significant amount of water. This module highlights the various solutions used in this facility to ensure water efficiency prerequisites were met while focusing on how to achieve a 2/3 water reduction over a typical laboratory. Solutions discussed include low water landscaping, low flow fixtures, grey water toilet systems, waterless urinals, cooling towers operating at night, condensate collection from cooling towers and solar array, and rainwater collection. Additionally this module discusses how the Venter Institute has prepared itself to incorporate purple pipe, grey water, and blackwater systems when municipality and regulatory changes are implemented.
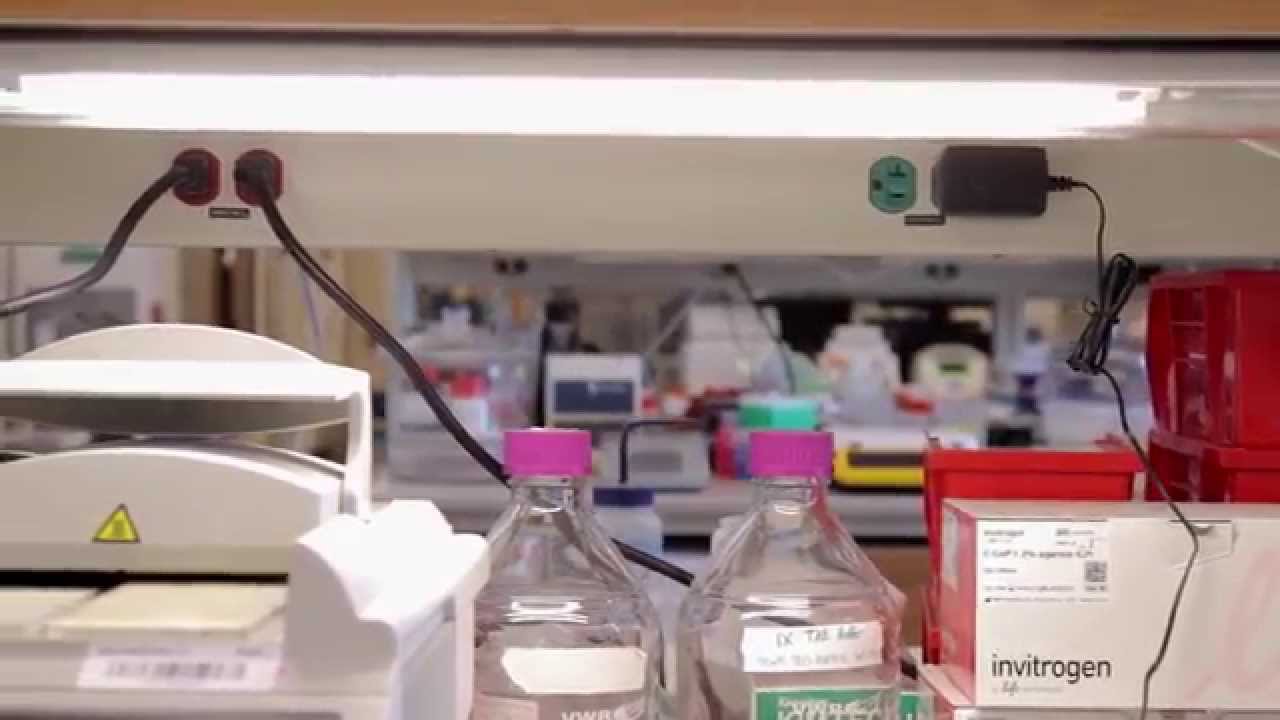
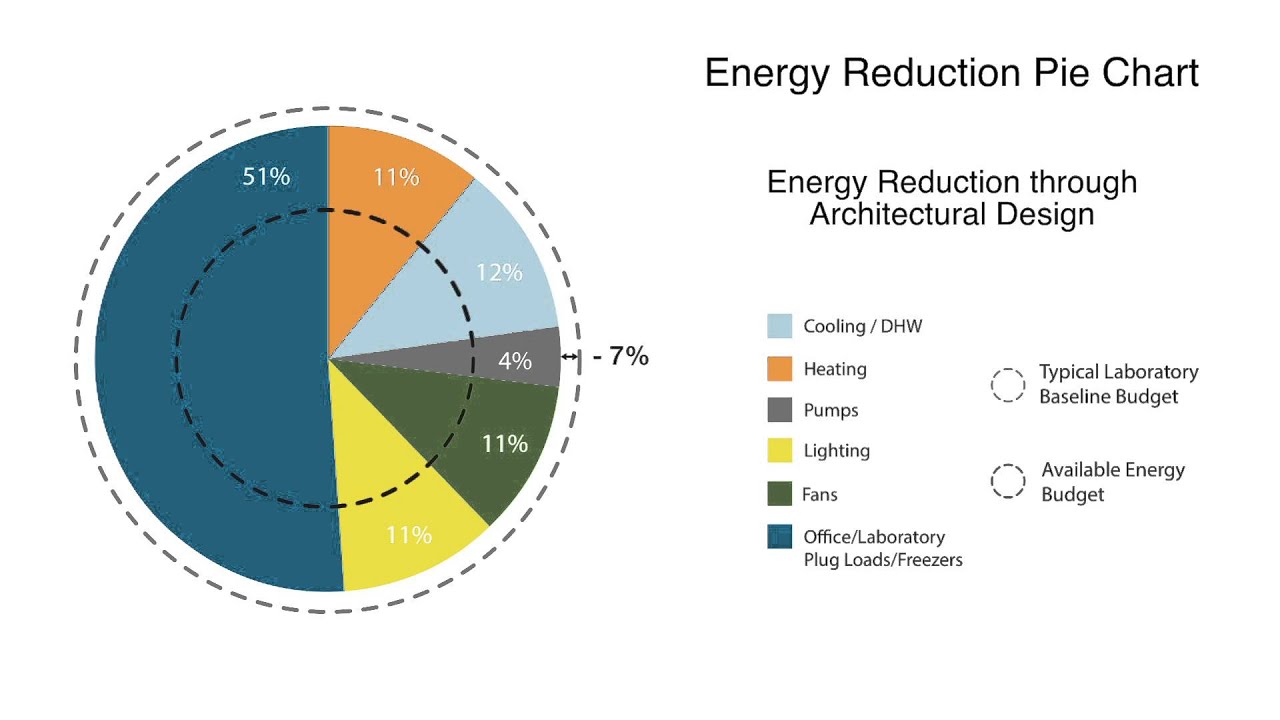
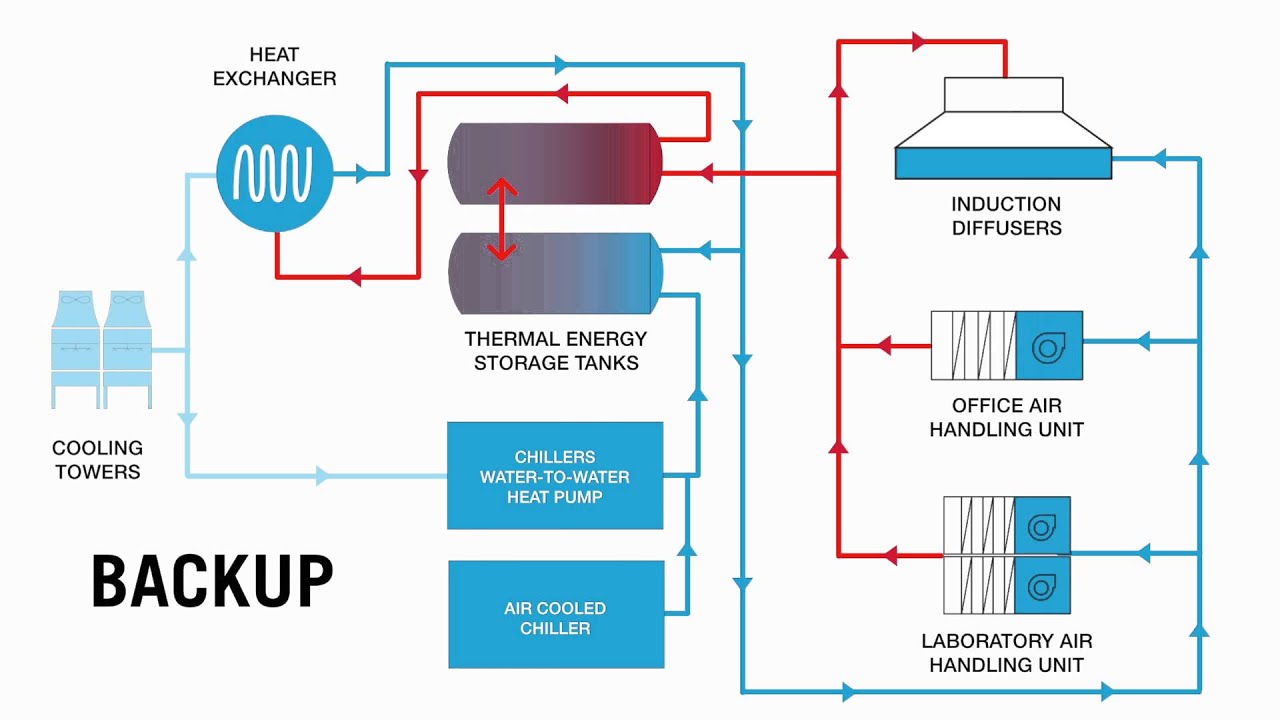
The Energy & Atmosphere credit looks at energy holistically and encourages maximum energy use reduction, energy efficient design strategies, and renewable energy sources. This was especially important for this project with laboratories typically using 5-10 times more energy than traditional office buildings. This module provides an insight and useful guide for maximizing energy efficiency and energy reduction. It discusses systems measuring, lighting, HVAC, the use of chilled beams, a co-located innovative freezer farm, the use of renewable energy (solar), and plug load management.
The Energy & Atmosphere credit looks at energy holistically and encourages maximum energy use reduction, energy efficient design strategies, and renewable energy sources. This was especially important for this project with laboratories typically using 5-10 times more energy than traditional office buildings. This module provides an insight and useful guide for maximizing energy efficiency and energy reduction. It discusses systems measuring, lighting, HVAC, the use of chilled beams, a co-located innovative freezer farm, the use of renewable energy (solar), and plug load management.
The Energy & Atmosphere credit looks at energy holistically and encourages maximum energy use reduction, energy efficient design strategies, and renewable energy sources. This was especially important for this project with laboratories typically using 5-10 times more energy than traditional office buildings. This module provides an insight and useful guide for maximizing energy efficiency and energy reduction. It discusses systems measuring, lighting, HVAC, the use of chilled beams, a co-located innovative freezer farm, the use of renewable energy (solar), and plug load management.
The Energy & Atmosphere credit looks at energy holistically and encourages maximum energy use reduction, energy efficient design strategies, and renewable energy sources. This was especially important for this project with laboratories typically using 5-10 times more energy than traditional office buildings. This module provides an insight and useful guide for maximizing energy efficiency and energy reduction. It discusses systems measuring, lighting, HVAC, the use of chilled beams, a co-located innovative freezer farm, the use of renewable energy (solar), and plug load management.
The Materials and Resource category focuses on minimizing embodied energy, and the impacts associated with extraction, processing, transport, maintenance, and disposal of building materials. This module highlights the materials and resources evaluation criteria and the selection process used in this project. Materials discussed include the wood selection, stainless steal, and concrete.
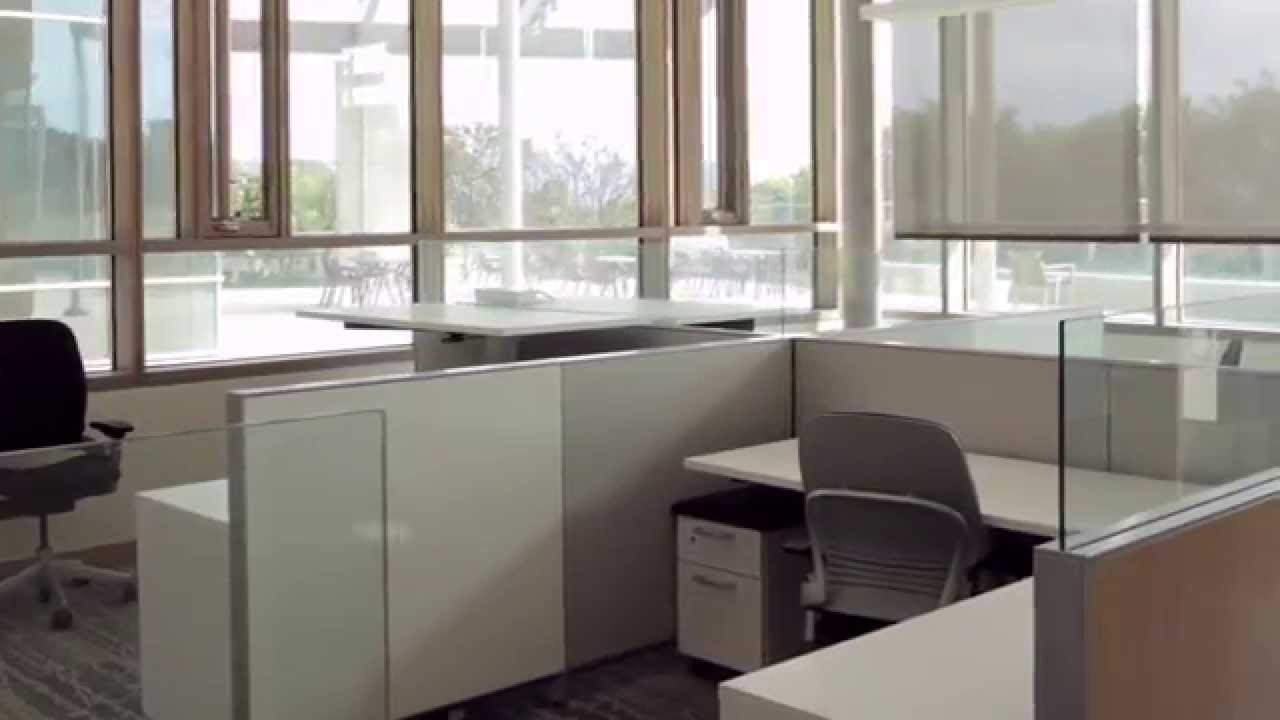
The Indoor Environmental Quality (EQ) category rewards decisions made by project teams about indoor air quality and thermal, visual, and acoustic comfort. This module highlights the solutions used in the Venter Institute to maximize indoor environmental quality, air quality, and user comfort. It also discusses the design of the space to foster collaboration among employees and guests. Topics covered include the collaborative design features, integration of outdoor workspaces and gathering places leveraging San Diego’s climate, the use of daylighting, scenic views of the ecological preserve and Pacific ocean, advanced air flow change strategies, operable windows associated with green light notification, ergonomic sit/stand work stations, open low wall work stations, modular and movable furniture, automated lighting and shade control.
The Indoor Environmental Quality (EQ) category rewards decisions made by project teams about indoor air quality and thermal, visual, and acoustic comfort. This module highlights the solutions used in the Venter Institute to maximize indoor environmental quality, air quality, and user comfort. It also discusses the design of the space to foster collaboration among employees and guests. Topics covered include the collaborative design features, integration of outdoor workspaces and gathering places leveraging San Diego’s climate, the use of daylighting, scenic views of the ecological preserve and Pacific ocean, advanced air flow change strategies, operable windows associated with green light notification, ergonomic sit/stand work stations, open low wall work stations, modular and movable furniture, automated lighting and shade control.
The Indoor Environmental Quality (EQ) category rewards decisions made by project teams about indoor air quality and thermal, visual, and acoustic comfort. This module highlights the solutions used in the Venter Institute to maximize indoor environmental quality, air quality, and user comfort. It also discusses the design of the space to foster collaboration among employees and guests. Topics covered include the collaborative design features, integration of outdoor workspaces and gathering places leveraging San Diego’s climate, the use of daylighting, scenic views of the ecological preserve and Pacific ocean, advanced air flow change strategies, operable windows associated with green light notification, ergonomic sit/stand work stations, open low wall work stations, modular and movable furniture, automated lighting and shade control.
Discover how some of the most innovative thinkers, designers, and engineers tackled new challenges and developed unique solutions to create the first net zero energy laboratory in the U.S. The team shares their insights and wisdom with others interested in implementing similar strategies as those found in the J. Craig Venter Institute.
Discover how some of the most innovative thinkers, designers, and engineers tackled new challenges and developed unique solutions to create the first net zero energy laboratory in the U.S. The team shares their insights and wisdom with others interested in implementing similar strategies as those found in the J. Craig Venter Institute.
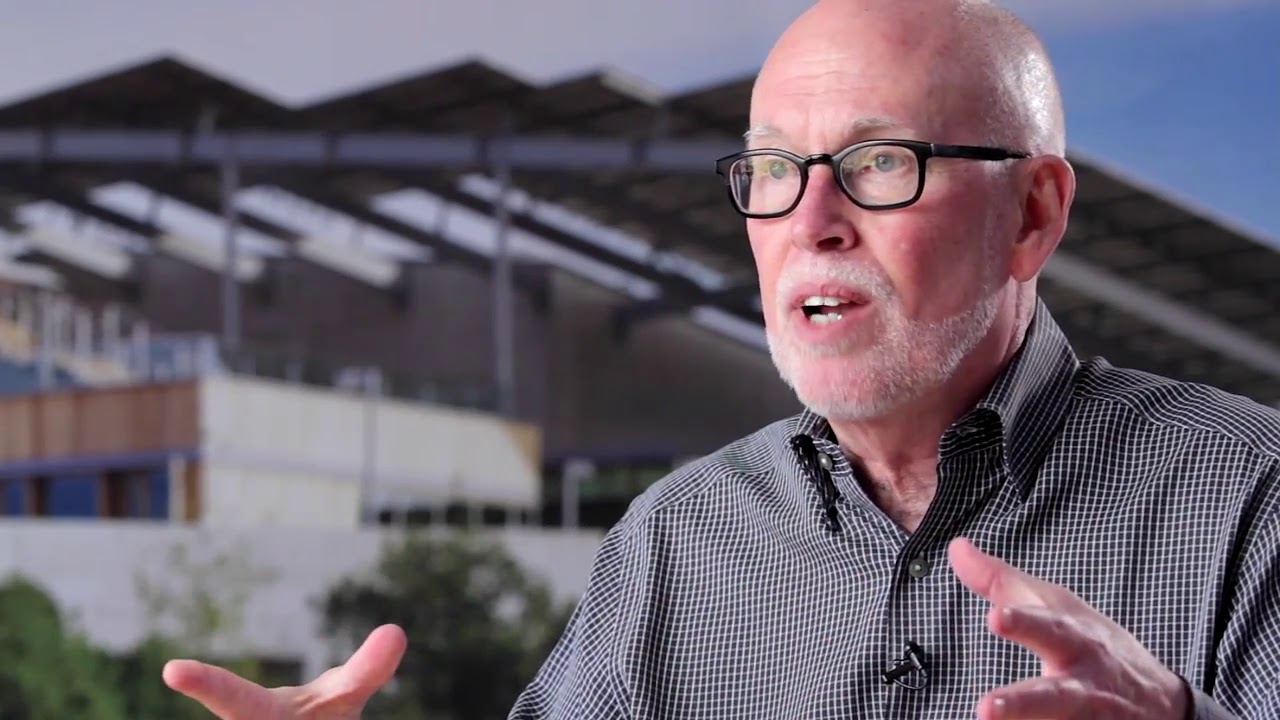
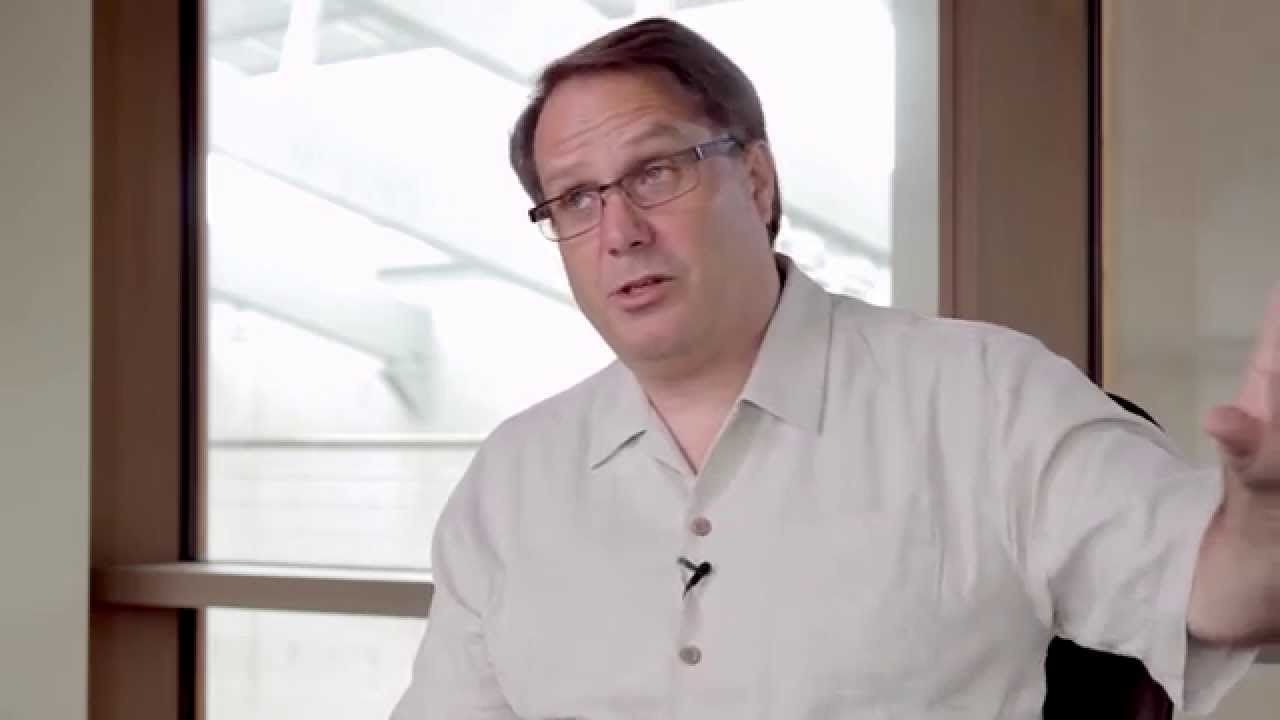
About Join Doss Mabe and Ted Hyman of ZGF Architects for a candid conversation about the integrative design process. Learn how a “what if” strategy was implemented and learn more about the planning, design, and development of the first net zero energy laboratory in the United States.
Instructional Video







